Difference between revisions of "Compactified Morse trajectory spaces"
From Polyfolds.org
m |
m |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
* Introduce smooth evaluation maps <math>{\rm ev}^\pm: \overline\mathcal{M}(\cdot,\cdot) \to L</math>, | * Introduce smooth evaluation maps <math>{\rm ev}^\pm: \overline\mathcal{M}(\cdot,\cdot) \to L</math>, | ||
* Define the length <math>\ell: \overline \mathcal{M}(L,L) \to [0,\infty]</math> by <math>\ell(\gamma)= a</math> for <math>\gamma: [0,a] \to L</math> and <math>\ell(\underline{\gamma})=\infty</math> for all generalized (''broken'') Morse trajectories <math>\underline{\gamma}</math> | * Define the length <math>\ell: \overline \mathcal{M}(L,L) \to [0,\infty]</math> by <math>\ell(\gamma)= a</math> for <math>\gamma: [0,a] \to L</math> and <math>\ell(\underline{\gamma})=\infty</math> for all generalized (''broken'') Morse trajectories <math>\underline{\gamma}</math> | ||
| + | * discuss boundary&corner stratification, in particular note that <math>L\subset \partial^1\overline\mathcal{M}(L,L)</math> (the set of trajectories with <math>\ell=0</math>) is isolated from all other boundary strata (made up of generalized trajectories with <math>\ell=\infty</math>) | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 6 June 2017
Consider a smooth manifold  equipped with a Morse function
equipped with a Morse function 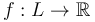 and a metric so that the gradient vector field
and a metric so that the gradient vector field  satisfies the Morse-Smale conditions. Then the Morse trajectory spaces
satisfies the Morse-Smale conditions. Then the Morse trajectory spaces
![{\begin{alignedat}{4}{\mathcal {M}}(L,L)&=\{\gamma :&[0,a]\;\;\to L&\,|\,{\dot \gamma }=-\nabla f(\gamma ),a\geq 0\},\\{\mathcal {M}}(p^{-},L)&=\{\gamma :&(-\infty ,0]\to L&\,|\,{\dot \gamma }=-\nabla f(\gamma ),\lim _{{s\to -\infty }}\gamma (s)=p^{-}\},\\{\mathcal {M}}(L,p^{+})&=\{\gamma :&[0,\infty )\;\to L&\,|\,{\dot \gamma }=-\nabla f(\gamma ),\lim _{{s\to +\infty }}\gamma (s)=p^{+}\},\\{\mathcal {M}}(p^{-},p^{+})&=\{\gamma :&\mathbb{R} \;\;\;\to L&\,|\,{\dot \gamma }=-\nabla f(\gamma ),\lim _{{s\to \pm \infty }}\gamma (s)=p^{\pm }\}/\mathbb{R} .\end{alignedat}}](/images/math/a/c/3/ac36e80abe76a15538933ab31effdc2f.png)
can - under an additional technical assumption specified in [1] - be compactified to smooth manifolds with boundary and corners  .
These compactifications are constructed such that the codimension-1 strata of the boundary are given by single breaking at a critical point (except in the first case we have to add one copy of
.
These compactifications are constructed such that the codimension-1 strata of the boundary are given by single breaking at a critical point (except in the first case we have to add one copy of  to represent trajectories of length 0),
to represent trajectories of length 0),

TODO:
- Introduce smooth evaluation maps
 ,
, - Define the length
![\ell :\overline {\mathcal {M}}(L,L)\to [0,\infty ]](/images/math/1/9/9/1999df464cac2fa6d20df6322ce81aea.png) by
by  for
for ![\gamma :[0,a]\to L](/images/math/e/2/7/e27331e5ae4baf6049fb5fd6dfbd06d7.png) and
and  for all generalized (broken) Morse trajectories
for all generalized (broken) Morse trajectories 
- discuss boundary&corner stratification, in particular note that
 (the set of trajectories with
(the set of trajectories with  ) is isolated from all other boundary strata (made up of generalized trajectories with
) is isolated from all other boundary strata (made up of generalized trajectories with  )
)